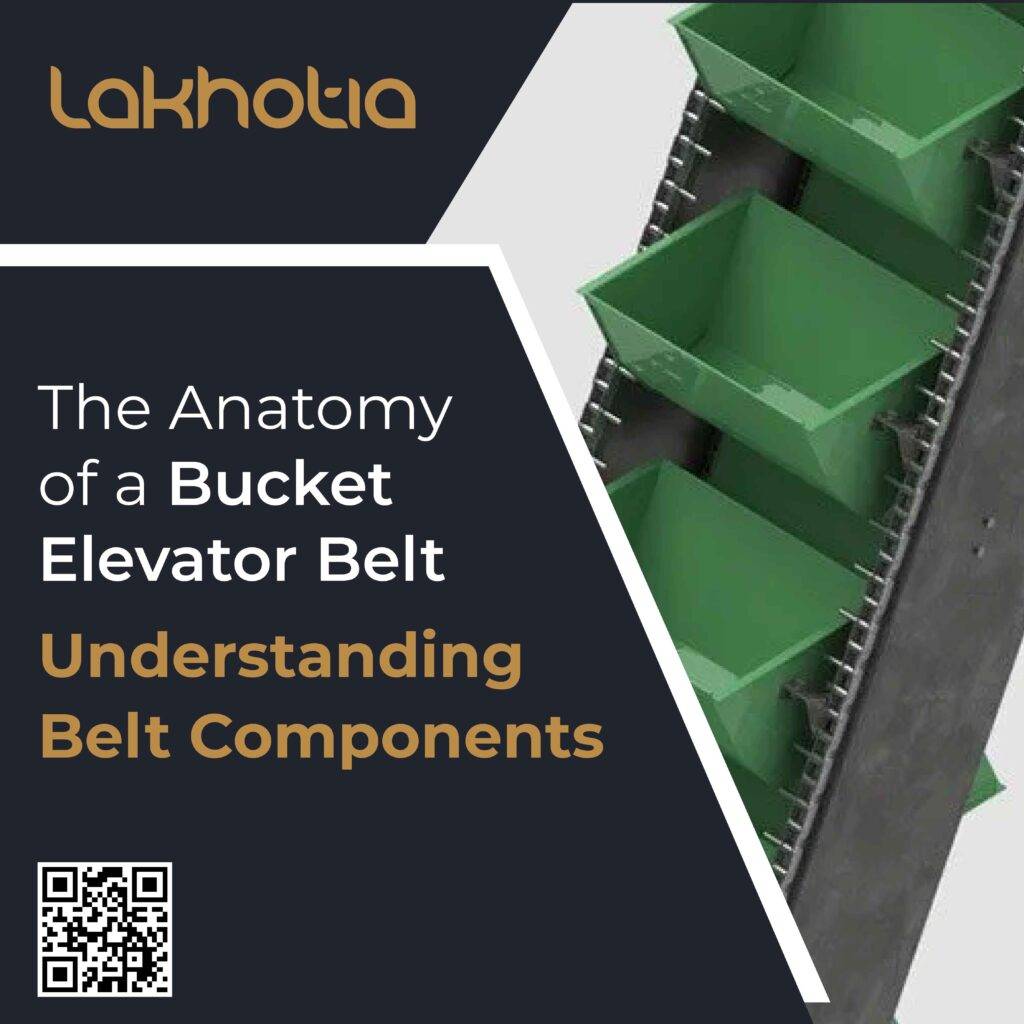
Understanding the anatomy of a bucket elevator belt is essential for anyone involved in the operation, maintenance, or design of material handling systems. These belts are complex structures designed to efficiently and safely transport various materials vertically. Here’s a breakdown of the key components that make up a typical bucket elevator belt:
The main body of the bucket elevator belt is typically made from various materials, including rubber, PVC, or synthetic compounds. The choice of material depends on factors such as the type of material being transported, environmental conditions, and the required belt strength.
The carcass or reinforcement layers are embedded within the belt material and provide strength, flexibility, and load-bearing capacity. They are typically made of textile fabrics, such as polyester, nylon, or steel cords, which are embedded between the layers of the belt material.
Cover layers are placed on both the top and bottom surfaces of the belt. These layers protect the carcass from wear, abrasion, and environmental factors. The covers can be made from different materials, including rubber, PVC, or other compounds, and their thickness and composition can vary depending on the application.
The buckets are containers attached to the belt at regular intervals. They are responsible for scooping up the material to be transported and depositing it at the discharge point. The shape and spacing of the buckets can vary based on the specific requirements of the application.
To secure the buckets to the belt, bucket attachments or fasteners are used. These can include bolts, rivets, or special clips. The attachment method must be robust to prevent buckets from dislodging during operation.
Belt fasteners are used to join the ends of the bucket elevator belt to create an endless loop. Proper installation of belt fasteners is critical to maintaining the integrity of the belt and ensuring safe operation.
Belt splices are where the two ends of the bucket elevator belt are joined together to create an endless loop. These splices need to be carefully executed to maintain the belt’s strength and flexibility.
Tensioning systems are used to maintain the appropriate tension in the belt. Proper tension is essential for efficient operation and to prevent belt slippage.
The pulleys are responsible for guiding the belt and transmitting power to move it. The drive system, which can include electric motors, gearboxes, and other components, provides the necessary force to move the belt and transport the materials.
These systems are used to ensure that the belt runs straight and true, preventing misalignment or eccentric loading, which can lead to wear and tear.
The structure or framework of the bucket elevator supports the belt, pulleys, and drive system. It is designed to withstand the vertical load and provide stability for the equipment.
Understanding the components of a bucket elevator belt is crucial for efficient and safe operation. Each component plays a vital role in the system’s efficiency and longevity. Regular inspection, maintenance, and proper care of these components are essential to ensure smooth and reliable material handling operations.